Solve the Differential Equation dy/dx=xy^2 In this tutorial we shall evaluate the simple differential equation of the form d y d x = x y 2 by using the method of separating the variables The differential equation of the form is given as d y d x = x y 2 Separating the variables, the given differential equation can be written asSimple and best practice solution for (x^2y^25)dx(yxy)dy=0 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve it Solve$$(x^22xyy^2)dy= (x^22xyy^2) dx $$ I've tried many methods but still unable to solve that problem Stack Exchange Network Stack Exchange network consists of 177 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers

Exact Differential Equations 2 6
X 2 y 2 dx x 2-xy dy 0 c1 x y 2 xe y/x
X 2 y 2 dx x 2-xy dy 0 c1 x y 2 xe y/x-Int (x^2 y^2 x y^3) dx dy, x=2 to 2, y=2 to 2 Extended Keyboard;How do I solve (X*22xyy*2) dx (y*22xyx*2) dy=0?



Http 1 160 97 198 8080 Xmlui Bitstream Handle 2 2 chapter 1 11 Pdf Sequence 2
1125am #1 Sydney Sales DE 2xy dx (y^2 x^2) dy = 0 2xydx ( y^2 x^2 ) dy = 0\\left( x 2y \right)dx \left( 2x y \right) dy = 0\ \ \Rightarrow \frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{x 2y}{2x y}\ This is a homogeneous differential equation y = (xlnx)/(1lnx) We have dy/dx = (x^2y^2xy)/x^2 with y(1)=0 Which is a First Order Nonlinear Ordinary Differential Equation Let us attempt a substitution of the form y = vx Differentiating wrt x and applying the product rule, we get dy/dx = v x(dv)/dx Substituting into the initial ODE we get v x(dv)/dx = (x^2(vx)^2x(vx))/x^2 Then assuming that x ne 0 this
The general solution of y^2dx (x^2 – xy y^2)dy = 0 is (A) tan^1(x/y) logy c = 0 asked in Differential equations by Sarita01 ( 535k points) differential equationsView this answer We are given (x2−y) dx(y2 −x) dy = 0 ( x 2 − y) d x ( y 2 − x) d y = 0 Rewrite x2 dx−y dxy2 dy−x dy = 0 x 2 d x − y d x y 2 d y − x d y = 0 RearrangeQuestion Verify That The Indicated Function Is A Solution Of The Givendifferential Equation Where Appropiate, C1 AndC2 Denote Constants27 (x2 Y2)dx (x2 Xy)dy= 0;
Solve the differential equation Best Answer This is the best answer based on feedback and ratings 100% (2 ratings) (xyy^2)dxx^2dy=0 y (xy) = x^2 dy / dx let y = View the full answer Previous question Next questionHomogeneous Differential Equation (y^2 yx)dx x^2dy = 0If you enjoyed this video please consider liking, sharing, and subscribingYou can also help suppor 113k views asked in Class XII Maths by nikita74 (1,017 points) Find the general solution of y 2 dx (x 2 xyy 2 )dy = 0 differential equations



Q Tbn And9gct7pqlrtcdooeregl7rlfrjdsu65gyfqxgwghfsugeb J Zgxkd Usqp Cau




The Solution Of 1 X 2 Dy Dx 2xy Xsqrt 1 X 2 0 Is A Y 1
C1(x Y)2 =xe(y/x)Simple and best practice solution for (Xy^2x)dx(yx^2y)dy=0 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework91 A product of several terms equals zero When a product of two or more terms equals zero, then at least one of the terms must be zero We shall now solve each term = 0 separately In other words, we are going to solve as many equations as there are terms in the product Any solution of term = 0 solves product = 0 as well




Exact Differential Equations 2 6
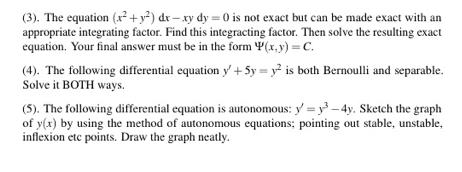



The Equation X 2 Y 2 Dx Xy Dy 0 Is Not Exact Chegg Com
It is homogeneous equationSolve $(2x^2 y^2)\,dx xy \, dy = 0$ Attempted The equation is not exact because $ M_y \ne N_x $ for $ M = 2x^2 y^2 $ and $ N = xy$ Or is it exact? From x dy dx y = x2y2, one can divide both sides by x so that it fits the Bernoulli form dy dx y x = xy2 Divide both sides by y2 y−2 dy dx 1 xy = x Then, define a function v = y1−2 = y−1 Differentiate both sides with respect to x to get dv dx = − dy dx y−2, or dy dx = − y2 dv dx



Http People Whitman Edu Hundledr Courses M244f12 M244 M244sol Pdf




Solucionario Ecuaciones1
Find dy/dx x^2xyy^2=1 Differentiate both sides of the equation Differentiate the left side of the equation Tap for more steps Differentiate Tap for more steps By the Sum Rule, the derivative of with respect to is Differentiate using the Power Rule which states that is whereThe differential equation is homogeneous Let mathy = ux/math Then mathdy = x \, du u \, dx/math and the equation becomes math(x^2 u^2 x^2) \, dx 2uxAn ordinary differential equation of first order and first degree can be written as dy dx = f(x,y) d y d x = f ( x, y) , where f(x,y) f ( x, y) is a function of two variables x,y x, y Which can




Calameo Ejercicios Resueltos Ecuaciones Diferenc




The Solution Of The Differential Equation 1 Y 2 X E Tan 1y
Simple and best practice solution for (x^2xyy^2)dx(xy)dy=0 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve it(c) given differential equation is (x x y^2) d x e^x^2 y d y = 0 x(1 y^2) d x = = e^x^2 y d y on spearing the variable we get y/ view the full answer Previous question Next question Transcribed Image Text from this QuestionRewrite the given equation as (y*dx x*dy) * (x^2 y^2) (y*dx x*dy) = 0 Eq(1) Divide throughout by (x^2 y^2) (y*dx x*dy) (y*dx x*dy) / (x^2 y^2




Solutions To Problems In Chapter One Mathematics



Www3 Nd Edu Craicu 1bspring10 Quiz1b Q10 Pdf
1 Answer1 Active Oldest Votes 1 ( x y) d x − ( x 2 y 2) d y = 0 Let F ( x, y) = x y and let G ( x, y) = x 2 y 2 Now consider a function u ( x, y) = 0 Then ∂ u ∂ x d x ∂ u ∂ y d yFind dy/dx x^2xyy^2=4 Differentiate both sides of the equation Differentiate the left side of the equation Tap for more steps Differentiate Tap for more steps By the Sum Rule, the derivative of with respect to is Differentiate using the Power Rule which states that is whereCompute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music



1



Pdf 2 6 Exact Differential Equations And Integrating Factors Mirna Mansour Academia Edu
The GS is y^2 = (A x^4)/(2x^2) Or, alternatively y = sqrt(A x^4)/(sqrt(2)x) We have (x^2 y^2) \\ dx xy \\ dy = 0 Which we can write in standard form as dy/dx = (x^2 y^2)/(xy) 1 Which is a nonseparable First Order Ordinary Differential Equation A suggestive substitution would be to perform a substitution of the form y = xv => dy/dx = v xv' \\ \\ \\ where v=v(xThe equation is also not separable The equation is also not homogenous, I don't think So what do I do? ∫∫f(x,y)dx dy =0=∫∫f(x,y)dy dx ist eben falsch Das habe ich auch bereits oben in meiner Antwort geschrieben Man kann auch ohne Polarkoordinaten rechnen und sieht, das alleine das erste Integral ∫(oo bis oo) x/(x^2 y^2)dx nicht konvergiert Lediglich der CauchyHauptwert ist 0 Weißt du, wie man uneigentliche Integrale berechnet?




Ecuaciones Diferenciales Lineales De Primer Orden Y Aplicaciones Tema



What Is The Exact Differential Equation Of X Y Dx X Y 1 Dy 0 Quora
Show that the differential equation (xy)dy/dx=x2y,is homogeneous and solve it asked in Mathematics by Nisa ( 597k points) differential equationsSimple and best practice solution for (x^2y^2)dx(x^2xy)dy=0 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve it Solve (y√(x^2y^2))dxxdy=0 Latest Problem Solving in Differential Equations More Questions in Differential Equations Online Questions and Answers in Differential Equations




X 2y 1 0 2x 3y 12 0 Novocom Top



The Solution Of Y 2xy E X Dx E Xdy 0 Is A X 2 Ye X C B Xy 2 E X C C Youtube
D x 2 ( x y) = 0 d x 2 ( x y) = 0 dx2(x y) = 0 d x 2 ( x y) = 0 Si cualquier factor individual en el lado izquierdo de la ecuación es igual a 0 0, la expresión completa será igual a 0 0 dx2 = 0 d x 2 = 0 xy = 0 x y = 0 Iguala el primer factor a 0 0 y resuelve Toca para ver más pasosAnswer to Solve the differential equation y(xy1) \, dx x(1xyx^2y^2) \, dy = 0 By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep solutions for Teachers for Schools for Working ScholarsSee the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer Previous question Next question Transcribed Image Text from this Question Solve dy/dx = x^2 xy y^2/x^2 Get more help from Chegg



Leangsimschoolboy Files Wordpress Com 13 09 Mat Advanced Engineering Mathematics Pdf




Verifying Solutions To Differential Equations Video Khan Academy
Solve the differential equation √(1 x^2 y^2 x^2y^2) xy(dy/dx) = 0 asked Mar 13 in Differential Equations by Yaad ( 352k points) differential equationsThe equation dx/y^2 = dy/x^2 = dz/(x^2)(z^2)y is the auxiliary system to obtain the general integral of the PDE (y^2)Z_x (x^2)Z_y = (x^2)(Z^2)y From the first two equations obtain dy/dx = x^2/y^2 which leads to the first integral Z1 = y^3 x^Simple and best practice solution for (4xxy^2)dx(yx^2y)dy=0 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve it



Http 1 160 97 198 8080 Xmlui Bitstream Handle 2 2 chapter 1 11 Pdf Sequence 2



Solve Dy Dx X 2 3y 2 2xy Youtube
Solve Dy/dx = X^2 Xy Y^2/x^2 Question Solve Dy/dx = X^2 Xy Y^2/x^2 This problem has been solved! But if I expand the bracket $(xy)^2$ before integrating I will get $$\varnothing_1=\int Mdx=\int (xy)^2dx=\int (x^22xyy^2)dx=\frac{x^3}{3}xy^2x^2y$$ Wich will lead to the solution $$\varnothing=\varnothing_1\varnothing_2=\frac{x^3}{3}xy^2x^2yy=Constant$$ What is the wrong step ? We can rearrange this Differential Equation as follows dy dx = − x2 y2 x2 − xy = − ( 1 x2)(x2 y2) ( 1 x2)(x2 −xy) = − 1 ( y x)2 1 − y x So Let us try a substitution, Let v = y x ⇒ y = vx Then dy dx = v x dv dx And substituting into the above DE, to eliminate y




First Order Differential Equations Chapter 2 Ch2 2 Contents 2 1 Solution Curves Without A Solution 2 1 Solution Curves Without A Solution 2 2 Separable Ppt Download



Www Math Uh Edu Almus 43 De Part1 After Pdf
Find dy/dx x^2y^2=2xy Differentiate both sides of the equation Differentiate the left side of the equation Tap for more steps Differentiate Tap for more steps By the Sum Rule, the derivative of with respect to is Differentiate using the Power Rule which states that is whereResolver para x (x^2y^2)dx (x^22xy)dy=0 (x2 − y2) dx (x2 − 2xy)dy = 0 ( x 2 y 2) d x ( x 2 2 x y) d y = 0 Factorizar la ecuación Toca para ver más pasos Factoriza d d a partir de d x ( x 2 − y 2) d y ( x 2 − 2 x y) d x ( x 2 y 2) d y ( x 2 2 x y) Toca para ver más pasos 1 Multiple by xayb so Mdx Ndy = 0 with M = xayb 1 xa 1yb 2, N = xa 1yb xa 2yb 1 xa 3yb 2 We choose a, b to achieve 0 = ∂yM − ∂xN = (b 1)xayb (b 2)xa 1yb 1 − (a 1)xayb − (a 2)xa 1yb 1 − (a 3)xa 2yb 2 = xayb((b − a)(1 xy) − (a 3)(xy)2) a = b = − 3 So 0 = Mdx Ndy = (x −



Pdf Complete Solutions Differential Equations With Modeling Applications Differential Equations With Boundary Value Problems 5th Edition Juan Carlos Becerra Linares Academia Edu




Second Order Linear Differential Equations
Dy/dx= (x^2y^2)/(3xy) The answer is supposed to be (x^2 4y^2)^3(x^2 )= CHere is what I have done x/(3y) y/(3x) = (1/3)(x/y y/x) = (1/3)(1/(y/x) y/x)Help is appreciated EditEcuacion diferencial de primer orden



How To Find The General Solution Of X 2y 2xy 2y Xe X Quora




Mathematics Xii Part 2 Pages 1 250 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5
` (x^(2)y^(2)) dx 2xy dy = 0`View this answer Given 2xy dx(x2−1) dy = 0 2 x y d x ( x 2 − 1) d y = 0 Rewrite 2xy dxx2 dy−1 dy = 0 2 x y d x x 2 d y − 1 d y = 0 Change the sides $$2 xy \ dx x^2 \ dy = 1
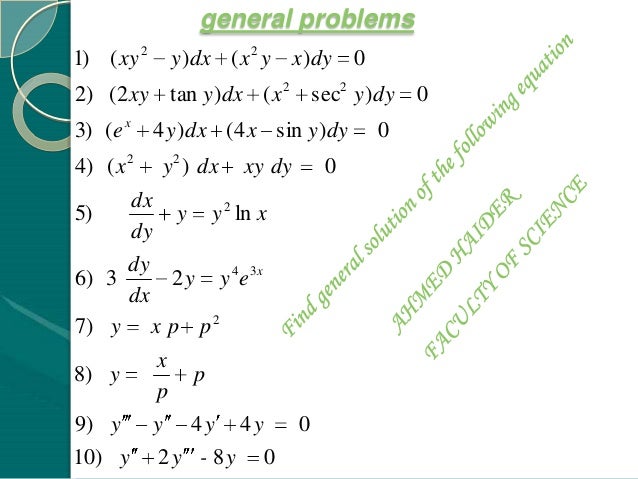



Ordinary Differential Equations



Www Ualberta Ca Rjia Math215 Hwks Sol1 Pdf




How To Solve Dx Dt 5x 2y T Dy Dt 2x Y 0 When X 0 Y 0 0 By Using Laplace Transformation Quora
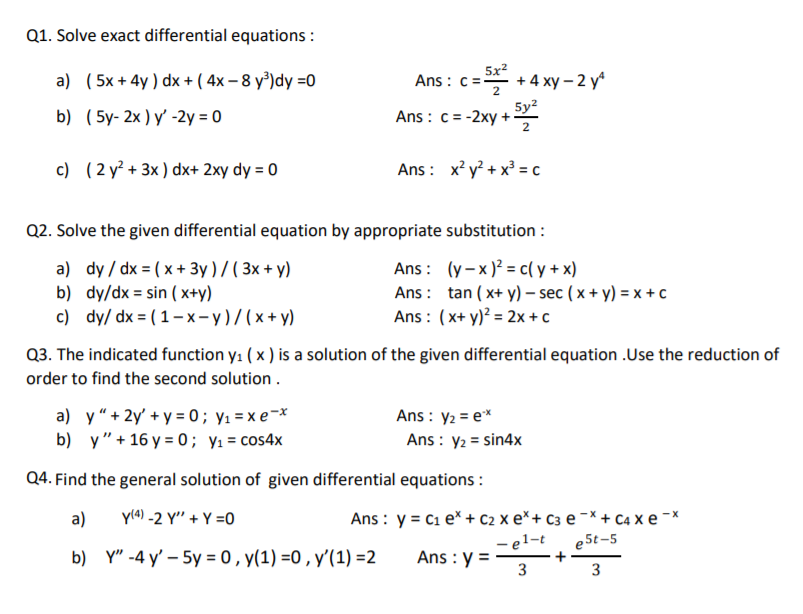



Q1 Solve Exact Differential Equations A 5x 4y Chegg Com




Ex 9 4 10 Find General Solution Ex Tan Y Dx 1 Ex




The Solution Of The Differential Equation Y Xy 2x 2y 2 Dx X Xy X 2y 2 Dy 0 Is Given Youtube




Ad Eng Math 6 8 15 Pages 51 100 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5




For The Differential Equation X 2 Y 2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Which Of The Following Are True Youtube



Http 1 160 97 198 8080 Xmlui Bitstream Handle 2 3 chapter 12 22 Pdf Sequence 3




X 2y 1 0 2x 3y 12 0 Novocom Top
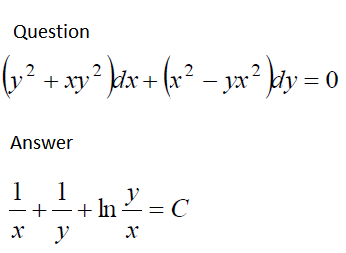



Question Y 2 Xy 2 Dx X 2 Yx 2 Dy 0 Answer Chegg Com




The Solution Of The Differential Equation 1 Y X 2y Dx X




Misc 14 Find Particular Solution X 1 Dy Dx 2e Y 1
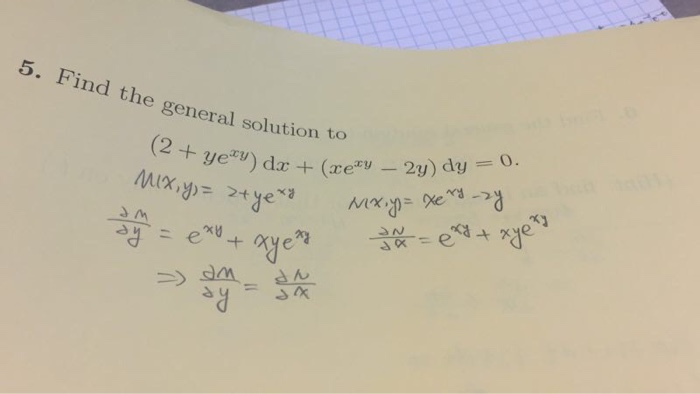



Find The General Solution To 2 Ye Xy Dx Xe Xy Chegg Com




The Differential Equation Xydx X 2 Y 2 Dy 0 Is Chegg Com



1



Http Www Math Sci Hokudai Ac Jp S Settepanella Teachingfile Calculus Calculus2 Pagine Lineintex Pdf



Solved 66 Exercise 9 Solve The Following Differential Equations Course Hero



What Is The General Solution Of The Ydx Xy 2 X Y Dy 0 Quora
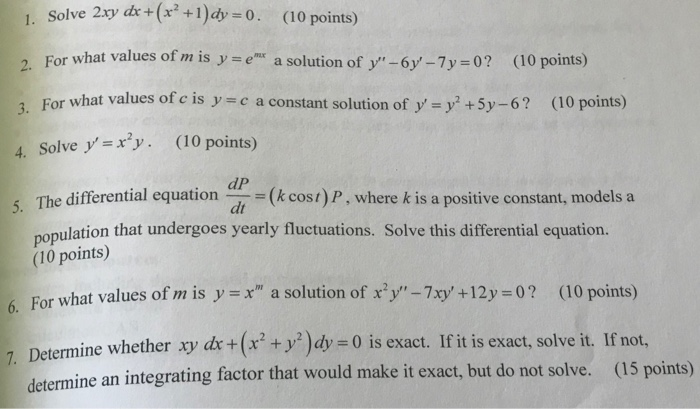



Determine Whether Xy Dx X 2 Y 2 Dy 0 Is Exact If Chegg Com



Http Www Math Sci Hokudai Ac Jp S Settepanella Teachingfile Calculus Calculus2 Pagine Lineintex Pdf




Ad Eng Math 6 8 15 Pages 51 100 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5




Exact Differential Equations
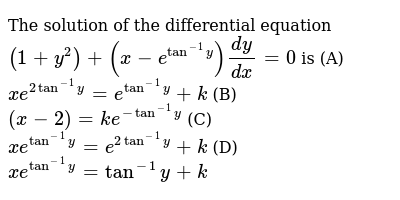



The Solution Of The Differential Equation 1 Y 2 X E Tan 1y




Solving Separable Differential Equations Calculus Socratic




How To Find Exact Equation Quick And Easy Differential Equations Explained Right Youtube




Misc 2 Verify Given Function Is A Solution Of Differential



Chapter 04 2500 Solved Problems In Differential Equations Docsity




Differential Equations Complete Manual Pdf Document




Differential Equations Mathematics Statistics And Calculus Solution Manual Docsity
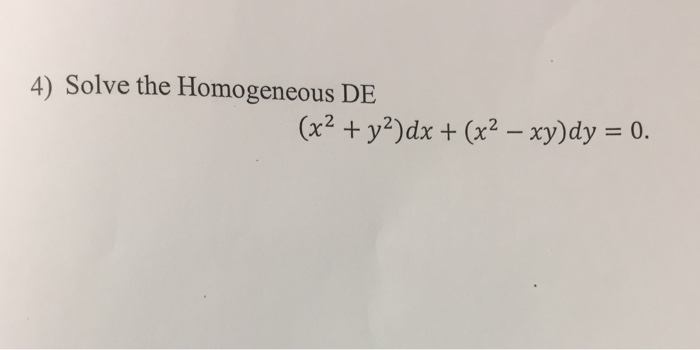



Solve The Homogeneous De X 2 Y 2 Dx X 2 Xy Dy Chegg Com




Ecuaciones Diferenciales Metodos De Solucion




Differential Equations With Boundary Value Problems 9th Edition By Zill Solution Manual Download By Mydexher Issuu



3 8 Implicit Differentiation Calculus Volume 1




3x Y Y 2 Dx X 2 X Y Dy 0



How To Solve This Differential Equation Dx Dy Ytany Xtany Xy Ytany Quora
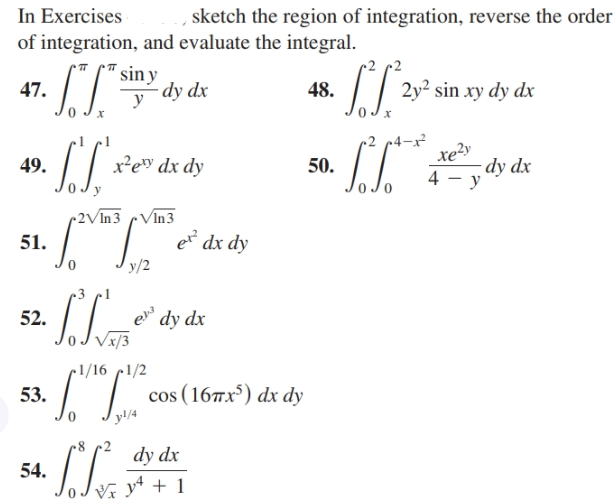



Answered In Exercises Of Integration And Bartleby



The Form Of The Exact Solution To 2 Dy Dx 3y E X Y0 5 Is A Ae 15x Be X C Ae 15x Course Hero




Let Y Y X Be The Solution Curve Of The Differential Equation Y 2 X Dydx 1 Satisfying Y 0 1 This Curve Intersects The X Axis At A Point Whose Obscissa Is




Tutorial Ode 1718 Trims 2 Ordinary Differential Equation Rates




If X 1 Y Y 1 X 0 Then Prove That 1 X 2 Dydx 1 0




First Order Differential Equations Ppt Download




Differential Equation
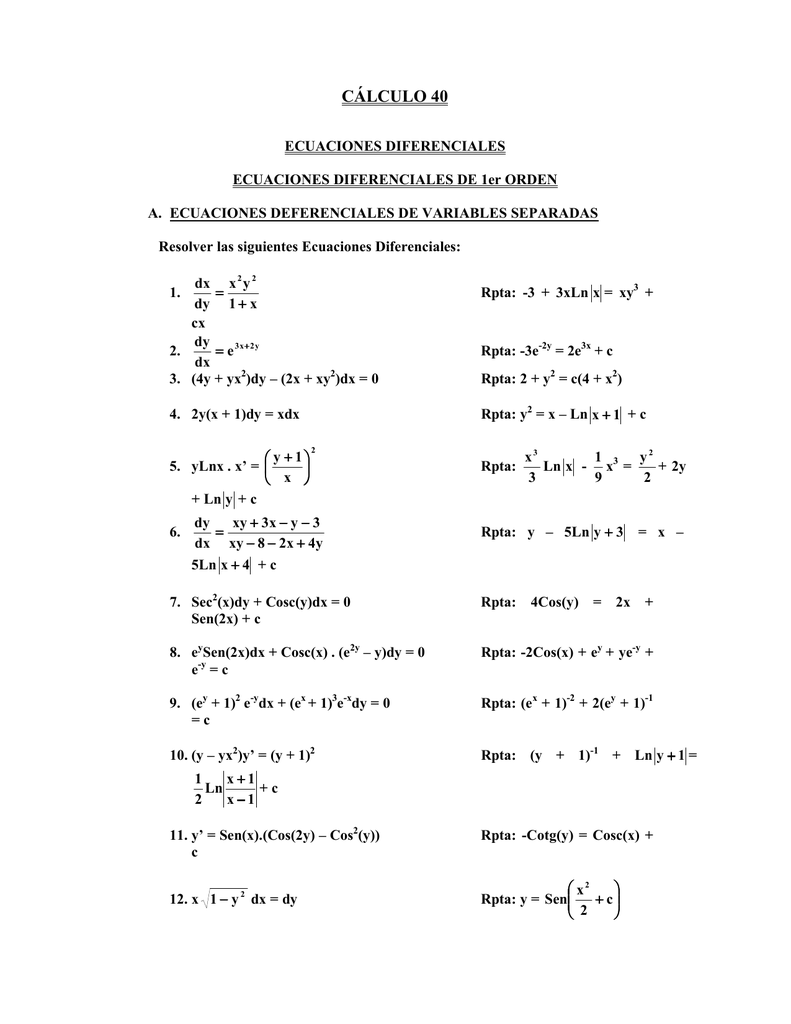



Calculo 40 Web Del Profesor




1 2e X Y Dx 2e X Y 1 X Y Dy 0 Novocom Top




Solution Manual 2nd Edition 1 Introduction To Differential Equations Exercises 1 1 1 Second Order Linear 2 Third Order Nonlinear Because Of Dy Dx 4 3 Course Hero



Dy Dx Xe Y X How Can I Solve The Above Differential Equation Quora




Ex 9 5 7 Show Homogeneous X Cos Y X Y Sin Y X Y Dx




Handouts Differential Equation And Advanced Mathematics Determinant Matrix Mathematics




Pdf Engineering Mathematics Ii 15mat21 Surya Karthik Academia Edu




1 First Order Ode S 18 03 Exercises 1a Introduction Separation Of Variables



Http Www Math Uiuc Edu G Choi1 285finalreviewsol 03 Pdf




Ecuaciones Diferenciales Homogeneas Xy Y 2 X 2 Dx X 2dy 0 La Prof Lina M3 Youtube



Http 1 160 97 198 8080 Xmlui Bitstream Handle 2 2 chapter 1 11 Pdf Sequence 2




Worked Example Separable Equations Differential Equations Video Khan Academy




1 Use Green S Theorem To Evaluate The Line Integral Chegg Com



Www Ualberta Ca Rjia Math215 Hwks Sol6 Pdf




Tutorial 7 Ordinary Differential Equation Equations




1 9 Fghbhj Equations Function Mathematics



Secure Media Collegeboard Org Digitalservices Pdf Ap Ap16 Calculus Q4 Pdf




Verify That Each Function Y F X Is A Solution Of Chegg Com




X Y Dx Dy 0 Novocom Top




Mergedpdf Ncert Csi 12 Math Split 2 Pages 151 0 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5




1 First Order Ode S 18 03 Exercises



1



Solve The Differential Equation X 2 Y 2 Dx 2xydy 0 Youtube
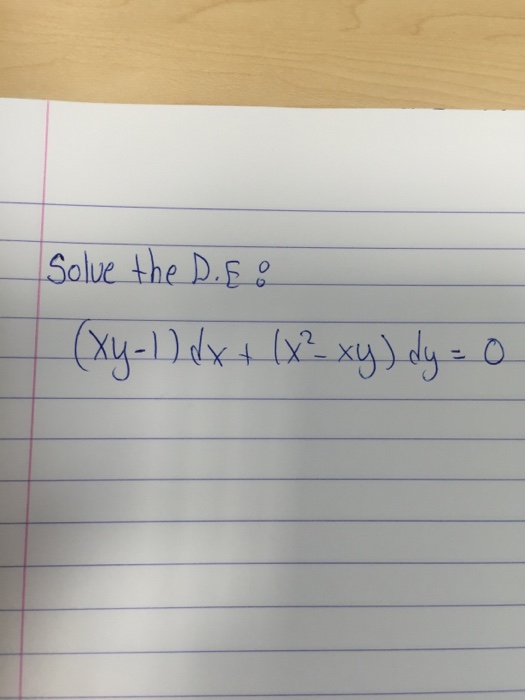



Solve The D E Xy 1 Dx X 2 Xy Dy 0 Chegg Com




Mathematics Xii Part 2 Pages 1 250 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5




Unit 03 Differential Equations Doc Logical Truth Equations
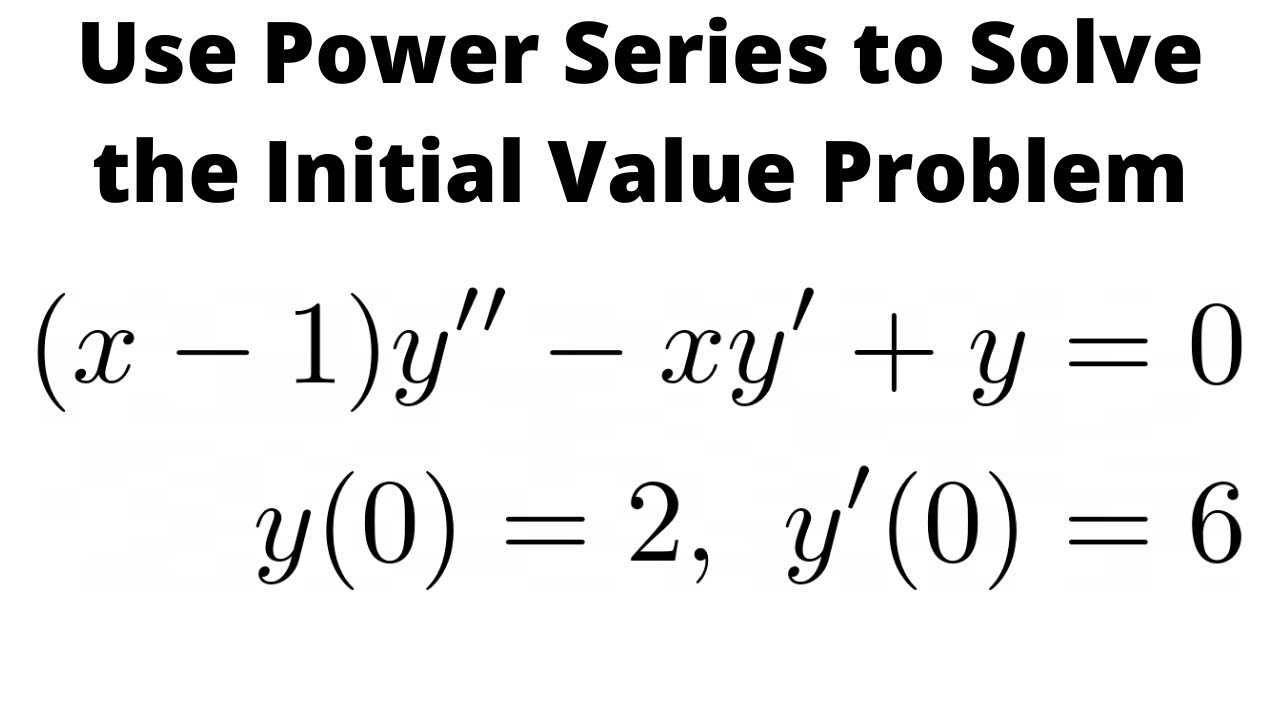



How To Solve A Differential Equation With Series X 1 Y Xy Y 0 With Y 0 2 Y 0 6 Youtube




Solutions Manual For First Course In Differential Equations With Modeling Applications 11th Edition By Mankiw234 Issuu




Differential Equations Module By Jessarina Olbes Issuu



Www Ualberta Ca Csproat Homework Math 334 Assignment solutions Assignment 1 solutions Pdf
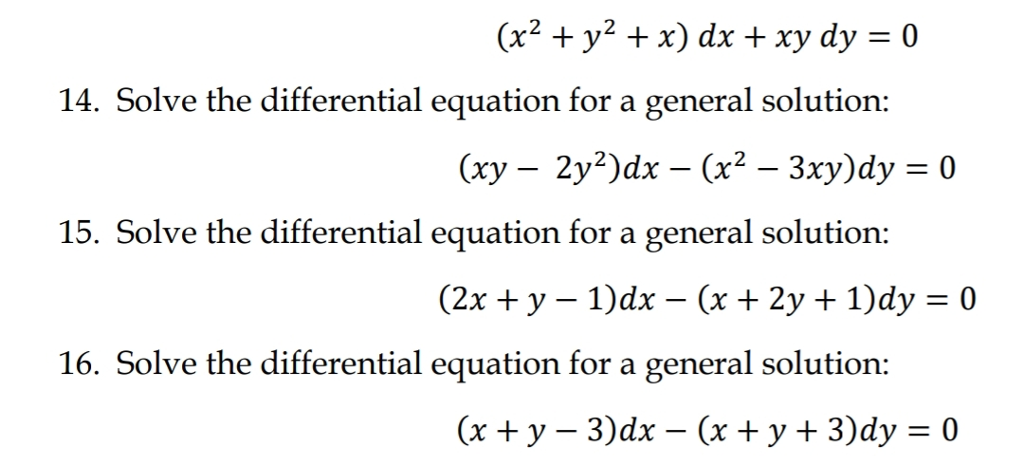



X2 Y2 X Dx Xy Dy 0 14 Solve The Differential Chegg Com



Http People Math Umass Edu Wchen M331 Midterm Sol Pdf



What Is The Solution Of Differential Equation D 2y Dx 2 2 Dy Dx Y 0 When X 0 Y 1 Dy Dx 2 Quora




3x Xy 2 Dx X 3 2y Dy 0 Y 0 2 Dy Dx Chegg Com



Http Www Iitg Ernet In Shyamashree Solution2 Pdf



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿